| Anmol Chemicals is the pioneer manufacturers of Magnesium Pidolate, Pharmaceutical Excipients Food & Flavor chemicals in India. We offer Halal and Kosher Magnesium Pidolate made in an ISO9001, ISO22000 (FSSC22000) cGMP and GLP certified facility. Our group has several manufacturing facilities spread across the world, supported by toll manufacturers and representatives in UAE, Europe, Africa, USA, China and has several associated manufacturing facilities spread across India. All the Information on Physics, Chemistry, Applications, Uses and Technology on Manufacture of Magnesium Pidolate is in these pages. |
| The units have one or more of the certifications like FDA GMP, ISO 9001, ISO 22000, HACCP, REACH, Kosher & Halal |




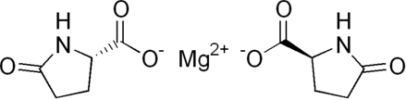
Magnesium Pidolate BP & Commercial Pure Grade Manufacturers
Specifications of Magnesium Pidolate (YOU ARE HERE)
Magnesium Pidolate SDS GHS MSDS Sheet
Magnesium Pidolate BP Grade
Ph Eur
C10H12N2O6Mg -- 280.5 -- CAS Number 62003-27-4
DEFINITION
Magnesium bis[(2S)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylate].
Content: 8.49 per cent to 8.84 per cent of Mg (Ar = 24.31) (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance: Amorphous, white or almost white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility: Very soluble in water, soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography.
Test solution: Dissolve 60 mg in 2 ml of water and dilute to 10 ml with methanol.
Reference solution: Dissolve 55 mg of pidolic acid CRS in 2 ml of water and dilute to 10 ml with methanol.
Plate:TLC silica gel plate.
Mobile phase: methanol, glacial acetic acid, methylene chloride (15:20:65 V/V/V).
Application:1 μl.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: At 100-105C for 15 min.
Detection: Spray with concentrated sodium hypochlorite solution. Allow to stand for 10 min and spray abundantly with glacial acetic acid. Allow to stand again for 10 min and dry the plate at 100-105C for 2 min. Spray with potassium iodide and starch solution until spots appear.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution. The chromatogram obtained with the test solution may show 2 faint secondary spots.
B. To 0.15 ml of solution S (see Tests) add 1.8 ml of water. The solution gives the reaction of magnesium.
TESTS
Solution S: Dissolve 5.00 g in carbon dioxide-free water prepared from distilled water and dilute to 50.0 ml with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution: Solution S is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution.
pH: 5.5 to 7.0 for solution S.
Specific optical rotation: - 23.3 to - 26.5 (anhydrous substance), determined on solution S.
Related substances:
Liquid chromatography.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.500 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 ml of the test solution to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 50.0 mg pidolate impurity B CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 ml of the solution to 50.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 10.0 ml of reference solution (b) to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 ml of nitrate standard solution (100 ppm NO3) to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (e): Dilute 6.0 ml of reference solution (a) to 10.0 ml with reference solution (b).
Column:
size: = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Dissolve 1.56 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 1000 ml of water R and adjust to pH 2.5 with a 10 per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate: 1.5 ml/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection: 10 μl loop injector; inject the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c), (d) and (e).
Run time: 4 times the retention time of pidolic acid.
Retention times: Pidolic acid = about 4.5 min; impurity B = about 7.5 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (e):resolution: minimum 10 between the peaks due to pidolic acid and to impurity B.
Limits:
impurity B: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
total of other impurities: not more than half of the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
disregard limit: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.05 per cent); disregard any peak corresponding to the nitrate ion (NO3–).
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in 4 ml of water and dilute to 50.0 ml with methanol.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 60.0 mg of glutamic acid R in 50 ml of water R and dilute to 100.0 ml with methanol. Dilute 1.0 ml of the solution to 20.0 ml with methanol.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of glutamic acid and 10 mg of aspartic acid in water and dilute to 25 ml with the same solvent. Dilute 1 ml of the solution to 10 ml with water.
Plate:TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid, water, butanol (20:20:60 V/V/V).
Application: 5 μl.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with ninhydrin solution and heat at 100-105C for 15 min.
System suitability: The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Limit:
impurity A: any spot corresponding to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is not more intense that the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.6 per cent).
Chlorides: Maximum 500 ppm.
Nitrates: Examine the chromatogram obtained with the test solution in the test for related substances.
Limit:
nitrates: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (200 ppm).
Sulphates: Maximum 0.1 per cent.
Arsenic: Maximum 2 ppm.
Iron: Maximum 200 ppm.
Heavy metals: Maximum 20 ppm.
Water: Maximum 8.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.300 g in 50 ml of water. Carry out the complexometric titration of magnesium.
1 ml of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 2.431 mg of Mg.
IMPURITIES
A. glutamic acid,
B. (2S)-2-[[[(2S)-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]pentanedioic acid.
For Original Monographs of IP Indian Pharmacopoeia BP British Pharmacopoeia USP US Pharmacopoeia FCC Food Grade product, please check with the respective web-pages or books.
Manufacturers
Anmol Chemicals
S-8, SARIFA MANSION, 2ND FLANK ROAD, CHINCHBUNDER, MUMBAI 400009, INDIA
TEL: (OFFICE) 91-22-23770100, 23726950, 23774610, 23723564. FAX: 91-22-23728264
e-mail: anmolc@mtnl.net.in

Exports to USA, Canada, UAE, Dubai, South Africa, Tanzania, Kenya, Nigeria, Egypt, Uganda, Turkey, Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Europe Netherlands, Italy, Spain, Germany, Portugal, France, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Korea, Japan, etc.
Copyright and Usual Disclaimer is Applicable. 29 January, 2022